Data Packets
They are the building blocks of the network. A packet is a basic unit of communication.
A packet is also called
- a datagram,
- a segment, a block,
- a cell, or a frame,
depending on the protocol used for data transmission.
Before data is transmitted, it is broken into smaller structures of data (packets).They are reassembled to the original data chunk after reaching their destination.
The structure of a packet depends on the type of packet and on the protocol.A packet has a header and a payload.
Header - It keeps overhead information about the packet, the service, and other transmission-related data.These include:
- Length of packet (like fixed-length packets (use classful subnetting - has fixed number hosts and networks)
- Synchronization (help the packet to match up with the network)
- Packet number (which packet this is in a sequence of packets)
- Protocol (defines what type of packet is being transmitted: e-mail, Web page,video streaming)
- Destination address
- Originating address (source)
Payload - is the bulk or body of the packet and carries the actual data.
If a packet is fixed-length, then the payload may be padded with blank information to make it the right size.
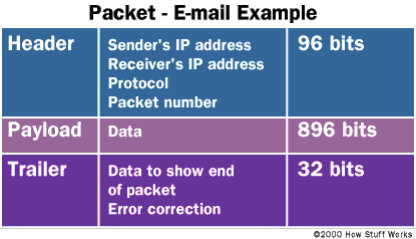
Trailer - also called the footer, typically contains a couple of bits that tell the receiving device that it has reached the end of the packet. It may also have some type of error checking.
This method of breaking data into smaller pieces (packet) and transmitting it over the network is called packet switching.
The IP packets travel over the internet through nodes (devices and routers) found on the way from the source to the destination. At each node, the router decides to which neighboring node it is more efficient to send the packet.
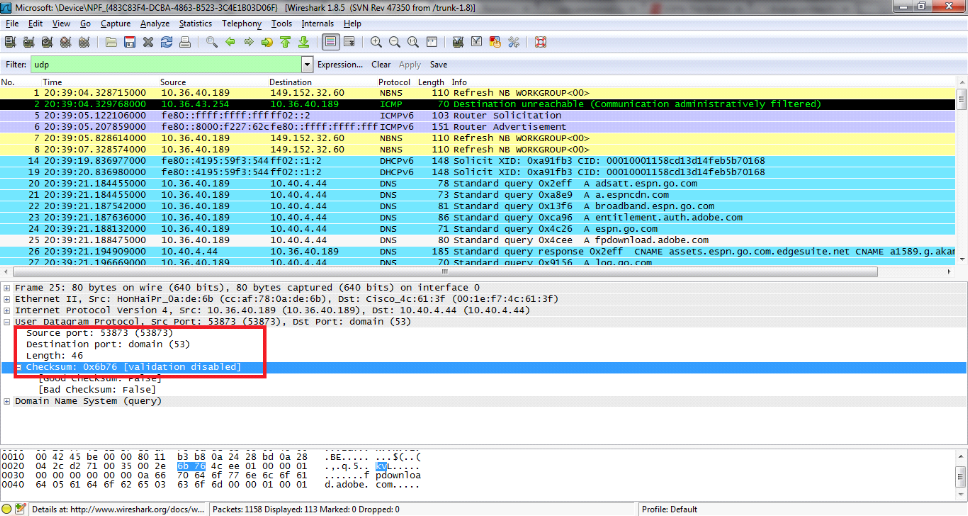
Packet Sniffer/Network Monitors/Protocol Analyzers
Packet sniffing means capturing data packets flowing across a computer network. The software or device used to do this is called a packet sniffer.
- A packet sniffer captures all of the packets of data that pass through a given network interface. In promiscuous mode, all packets travelling through the network will be captured regardless of destination.
- It is used by network or system administrator to monitor and troubleshoot network traffic.

Attackers can use it for:
- To capture username and passwords and authentication tokens (if transmitted in clear or plain text - means unencrypted)
- Website visited and what the user viewed on the site
- Packets captured can be used for later playback in replay, man-in-the-middle and packet injection attacks
Countermeasure:
- Use encryption like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) to protect your network traffic.
- Encryption doesn't prevent packet sniffers from seeing source and destination information, but it does encrypt the data packet's payload so that all the sniffer sees is encrypted gibberish.
- Any attempt to modify or inject data into the packets fails because messing with the encrypted data causes errors at the other end
PROTOCOLS
A protocol is a standard set of rules that allow electronic devices to communicate with each other. These rules include what type of data may be transmitted, what commands are used to send and receive data, and how data transfers are confirmed.
It is like a spoken language. If two hardware devices support the same protocol, they can communicate with each other. There are different Protocols for several applications.
Example:
- Ethernet for wired networking
- 802.11ac for wireless networking
- IP for Internet communication
The Internet protocol suite(TCP/IP), which is used for transmitting data over the Internet, contains dozens of protocols. These protocols may be broken up into four catagories:
- Link layer - PPP, DSL, Wi-Fi, etc.
- Internet layer - IPv4, IPv6, etc.
- Transport layer - TCP, UDP, etc.
- Application layer - HTTP, IMAP, FTP, etc.
Ex: UDP Encapsulation
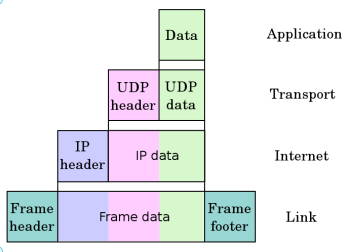
- Link layer protocols establish communication between devices at a hardware level. In order to transmit data from one device to another, each device's hardware must support the same link layer protocol.
- Internet layer protocols are used to initiate data transfers and route them over the Internet.
- Transport layer protocols define how packets are sent, received, and confirmed.
- Application layer protocols contain commands for specific applications. For example, a web browser uses HTTPS to securely download the contents of a webpage from a web server.
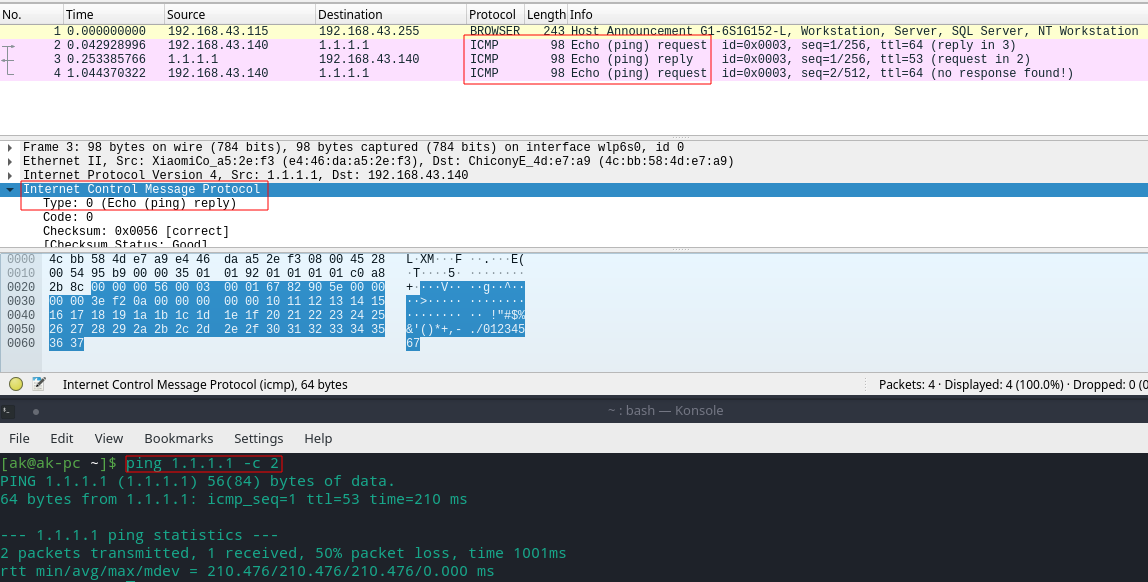
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
It is used by network devices to diagnose network communication issues,to determine whether or not data is reaching its intended destination in a timely manner. It’s primary purpose is error reporting.
- If there is a problem with the connection, error and status messages regarding the connection are sent using ICMP, which is part of the Internet protocol.
- It is commonly used in network devices like router
The two most common troubleshooting tools that utilize ICMP are:
- Traceroute
- Packet Internet Groper (ping)
- Traceroute command is used to discover the routes that packets actually take when traveling to their destination. Traceroute will not only identify each router the packet has been forwarded through, but will also measure the delay experienced at each router hop.The journey between one router and another is known as a ‘hop’
- It traces the entire path that a packet travels through
- Get Names and identity of routers and devices in the path
- It measures Network Latency or more specifically the time taken to send and receive data to each devices on the path
How Traceroute works?
- Each IP packet that you send on the internet has got a field called as TTL. TTL stands for Time To Live.TTL is not measured by the num of seconds but by the num of hops. Its the maximum number of hops that a packet can travel through across the internet, before it is discarded.
- TTL value is set by the sender inside his IP packet (happens under the hood).If the destination is not found TTL value becomes 0 (which means no further travel) the receiving router will drop the packet and informs the original sender.
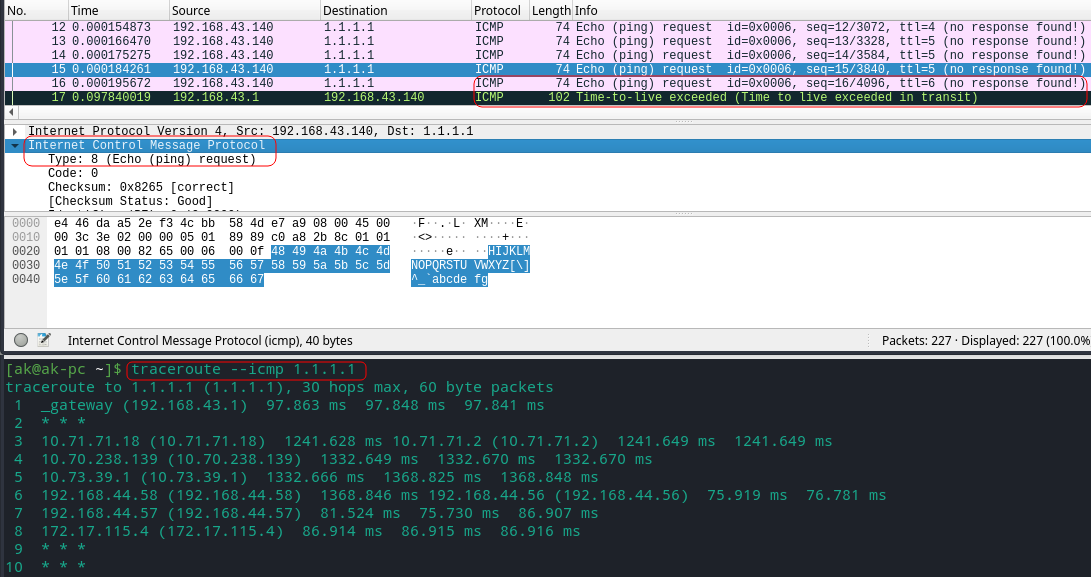
- Each router that comes in between the source and destination will go on reducing the TTL value before sending to the next router. It means if a packet has TTL value of 30, then the first router will reduce it to 29 and then send that to the next router.The router which discards the packet will inform the original sender that the TTL value has exceeded
-
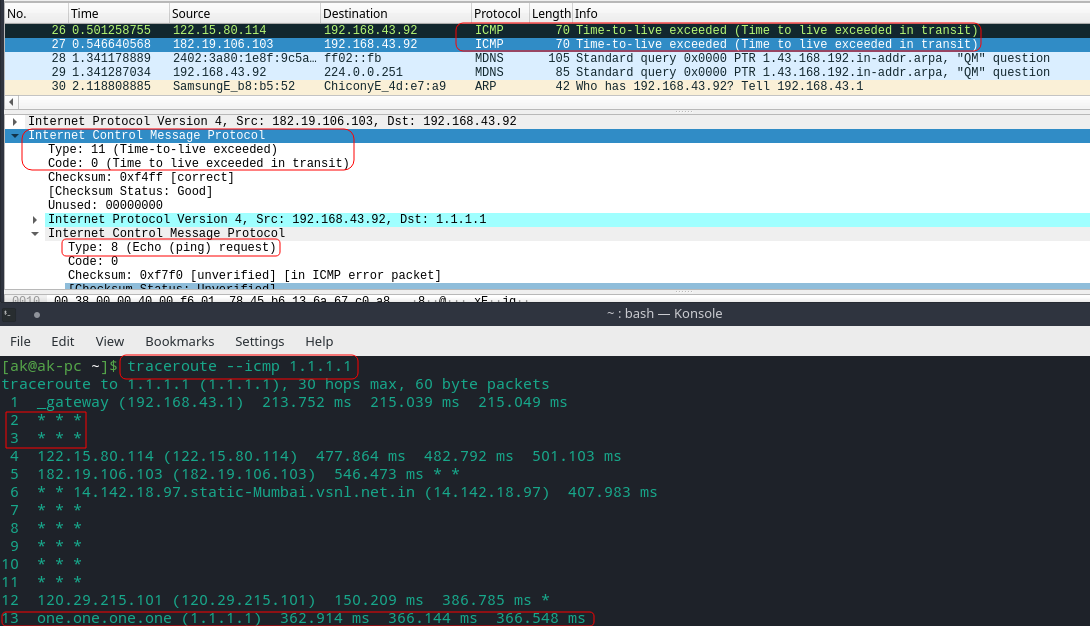
If you receive '* * *', this could mean that the router in the path
a) does not return ICMP messages,
b) it returns messages with a TTL too small to reach your machine
OR c) a router with buggy software.
After a ' * * *' within the path, traceroute will still increase the TTL by 1, thus still continuing on in the path determination. -
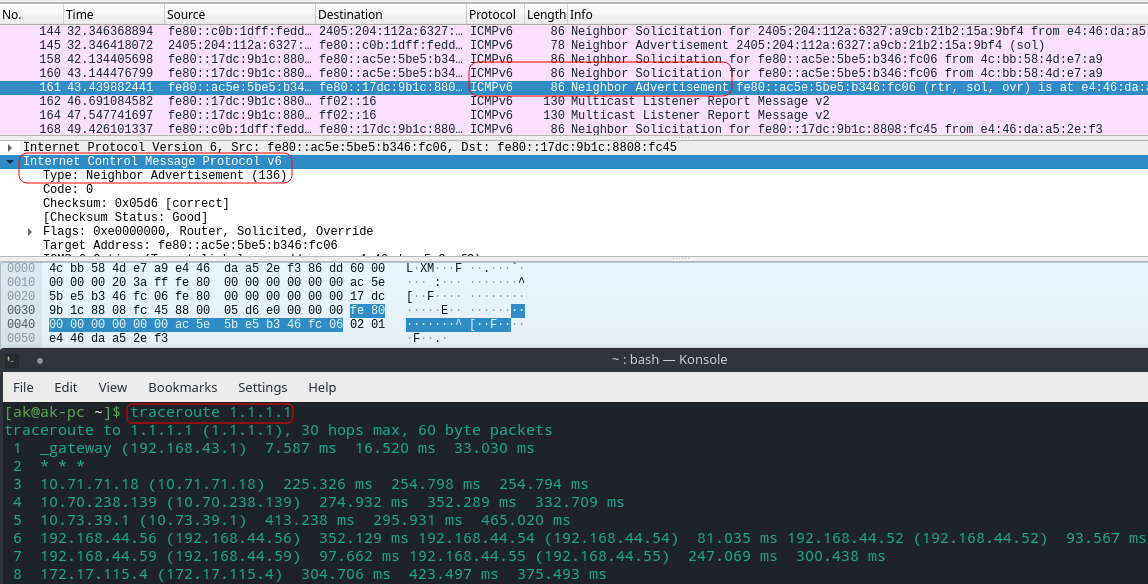
Traceroute will use ICMPv6 Packets if normal ICMP packets which works with IPv4 will not be able to reach the destination(Port).
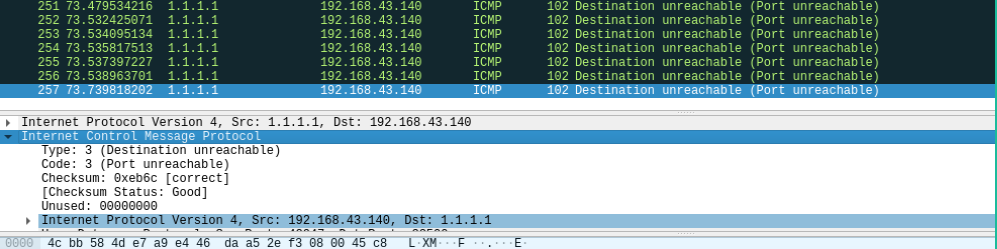
- Ping - The ping utility is a simplified version of traceroute,use to test speed of the connection.(<30ms - fast, 30-50ms -average).It also tell us about packet loss.It utilizes the Echo Request and Echo Reply ICMP messages to determine if an IP address is reachable and responding. Unfortunately network attacks can exploit this process,such as the ICMP Flood Attack and the Ping of Death attack.
How ping works?
The ping command first sends an echo request packet to an IP address, then waits for a reply. The ping is successful only if:
- The echo request gets to the destination
- The destination is able to get an echo reply back to the source within a predetermined time called a timeout.
Ex: The default value of this timeout is two seconds on Cisco routers.